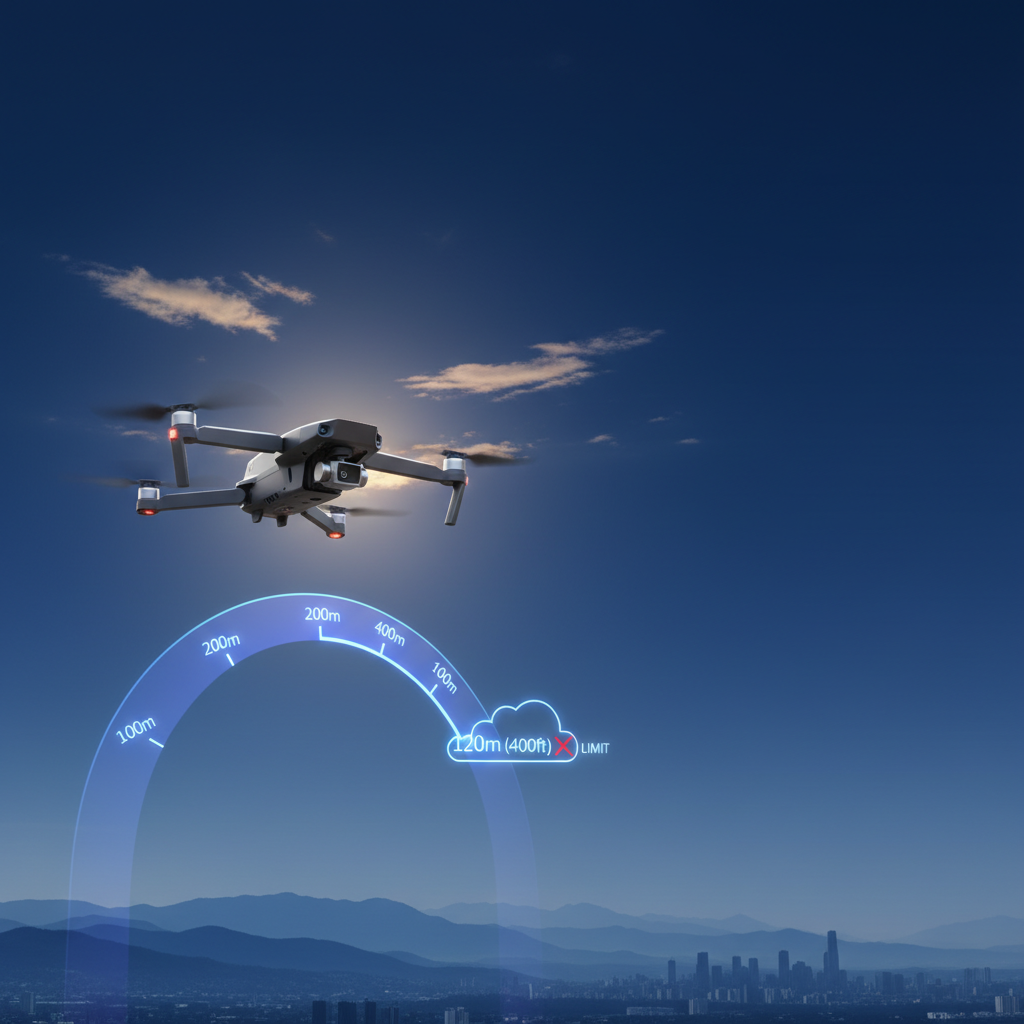
Drones can typically fly at altitudes ranging from 400 to 500 feet above ground level. However, various factors influence their maximum flight height, including regulations, drone type, and environmental conditions. Understanding these aspects is essential for anyone looking to operate drones safely and effectively. In this article, we will explore these factors in detail to help you comprehend the altitude limits for different drones.
Understanding FAA Regulations
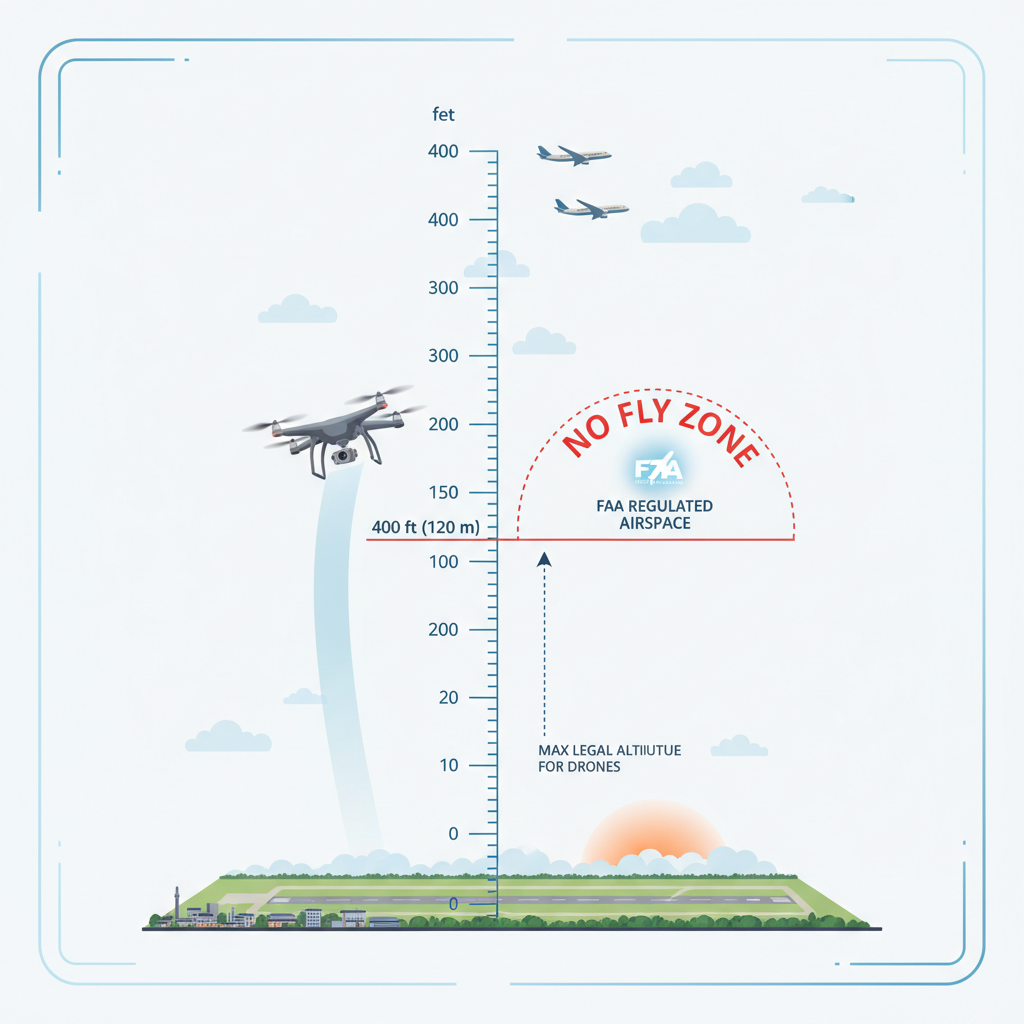
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) plays a critical role in regulating drone usage in the United States, including altitude limits. For safety and effective airspace management, the FAA has capped the maximum altitude for drone flights at 400 feet above ground level (AGL) for most recreational and commercial drones. This limit helps prevent collisions with manned aircraft, which typically operate at higher altitudes.
In addition to the 400-foot limit, the FAA also imposes restrictions based on the type of airspace in which the drone is operating. For instance, flying in controlled airspace, such as near airports, requires specific permissions and adherence to additional regulations. Furthermore, drone operators must maintain a visual line of sight with their drones at all times, which further ensures safety and compliance with regulations. Understanding these FAA regulations is crucial for any drone operator, as violations can lead to severe penalties, including fines or the revocation of flying privileges.
Types of Drones and Their Altitude Capabilities

The type of drone being used can significantly affect its altitude capabilities. Consumer drones, commonly used for recreational purposes or light photography, are generally designed to adhere to the 400-foot limit set by the FAA. Popular models like the DJI Mavic Air 2 and the Parrot Anafi typically feature maximum altitude settings around this threshold, ensuring compliance with regulations while providing sufficient altitude for capturing aerial images.
On the other hand, professional and racing drones may be engineered to reach greater heights, especially under specific conditions. For instance, racing drones, built for speed and agility, can exceed typical altitude limits in competitive environments where such flights are permitted. Some high-performance drones, designed for industrial applications, may also be equipped with advanced technology that allows for flights above standard limits, assuming they are operated in compliance with local regulations and safety measures. Knowing the capabilities of your drone type is essential for maximizing its potential while adhering to legal restrictions.
Environmental Factors Affecting Flight Height
Environmental conditions can significantly influence a drone’s maximum flight height. Weather factors such as wind speed, humidity, and temperature play a vital role in determining how high a drone can safely ascend. High winds, for instance, can make it challenging to maintain stability at elevated altitudes and could lead to loss of control. Similarly, adverse weather conditions, such as rain or fog, can impair visibility and drone performance, restricting effective flight height.
Moreover, physical obstacles in the environment can also limit accessible altitude. Trees, buildings, and other structures can create no-fly zones or areas where safe operation becomes challenging. Drone pilots must assess their surroundings carefully to avoid collisions and ensure a safe flying experience. Utilizing mapping applications and drone navigation tools can help operators identify potential obstacles and plan their flight paths effectively.
Technology Limitations and Enhancements
The technology embedded in drones significantly affects their altitude capabilities. Factors such as battery life, motor power, and onboard sensors can determine how high and how long a drone can fly. Standard consumer drones are often limited in altitude due to battery constraints that dictate the maximum operational height and time in the air. For instance, a drone that can reach 400 feet may only sustain that height for a limited duration due to battery drain.
Advanced drones, however, are increasingly equipped with features such as GPS, altitude hold functions, and advanced stabilization systems that enhance their performance at higher altitudes. These technologies enable drones to maintain a steady altitude, even in windy conditions, and can facilitate higher operational efficiency. Moreover, some cutting-edge drones are designed to automatically adjust their flight altitude based on real-time environmental data, allowing for safer and more reliable operations. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even greater advancements in drone flight capabilities.
Safety Considerations When Flying Drones
Safety should always be a top priority for drone operators, especially when it comes to altitude limits. Keeping a visual line of sight with the drone is crucial for safe operation. This means that operators should always be able to see their drone in the sky and be aware of its surroundings to avoid potential collisions with other aircraft or obstacles.
Additionally, awareness of no-fly zones and other airspace restrictions is essential for responsible flying. The FAA provides resources such as the B4UFLY app, which helps operators identify restricted airspace before launching their drones. Understanding these regulations not only ensures compliance but also enhances the safety of all airspace users. Furthermore, operators should conduct pre-flight checks to ensure their drones are in good working condition, including battery levels and functional components, to minimize the risks associated with altitude flying.
Future Developments in Drone Technology
As drone technology continues to advance, there are several exciting developments on the horizon that may enable drones to fly higher and safer. Innovations in battery technology, for example, could lead to longer flight times and increased altitude capabilities. Enhanced sensors and AI-driven navigation systems could also provide drones with the ability to detect and avoid obstacles more effectively, thereby allowing them to operate safely at higher altitudes.
Moreover, regulatory changes may also play a role in expanding permissible altitude limits in the future. As the drone industry grows and more data is collected regarding safe operations, we may see a shift in regulations that allows for greater altitude capabilities under certain conditions. Staying informed about these developments is essential for drone operators looking to maximize their flying experience while adhering to safety standards.
In conclusion, while most drones are limited to a maximum altitude of around 400 feet, various factors such as regulations, drone type, environmental conditions, technology capabilities, and safety considerations all play vital roles in determining the actual flight height. Understanding these elements will help you fly your drone safely and effectively. As drone technology continues to evolve, staying informed about advancements and regulatory changes will enable operators to make the most out of their flying experience while ensuring compliance and safety in the skies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the legal maximum altitude for drones in the United States?
In the United States, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) regulates that drones must not fly higher than 400 feet above ground level when operating in uncontrolled airspace. If you are flying near a structure, you can fly up to 400 feet above the highest point of the structure. It’s essential to adhere to these regulations to ensure safety and compliance with aviation laws.
How high can consumer drones typically fly?
Most consumer drones are designed to fly at altitudes ranging from 300 to 400 feet. However, many models have a maximum operational ceiling that can exceed 400 feet, depending on the manufacturer’s specifications. Users should always check their drone’s manual for the exact maximum altitude and ensure they operate within legal limits to avoid interference with manned aircraft.
Why do drones have altitude limitations?
Drones have altitude limitations primarily for safety and regulatory reasons. These restrictions are in place to prevent collisions with manned aircraft, which typically fly at higher altitudes. Additionally, maintaining controlled airspace ensures that drones do not disrupt air traffic, promoting safe and responsible flying practices among recreational and commercial drone operators.
Which drones can fly the highest, and what factors affect their altitude?
High-end commercial drones, such as the DJI Matrice series or the Yuneec Typhoon H, can often fly above the standard 400-foot limit, with some capable of reaching altitudes of 10,000 feet under specific conditions. Factors affecting a drone’s altitude include its design, weight, battery power, and environmental conditions like wind and temperature. Always verify local regulations before attempting to fly at higher altitudes.
What should I do if I want to fly my drone higher than the legal limit?
If you’re considering flying your drone at altitudes higher than the legal limit, it’s crucial to first obtain the necessary permissions from the FAA or relevant aviation authority. You may need to apply for a Special Airworthiness Certificate or use the FAA’s Part 107 exemption process for commercial purposes. Always prioritize safety and ensure you are fully compliant with regulations before attempting high-altitude flights.
References
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Drone
- https://www.faa.gov/uas/getting_started/part_107
- https://www.nasa.gov/centers/dryden/pdf/86556.pdf
- https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2022/nov/01/drone-regulations-uk-usa
- https://www.reuters.com/technology/drones-fly-high-into-urban-future-2021-07-15/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352864821002076
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8689422/
- https://www.cnn.com/2022/02/01/tech/drone-altitude-restrictions/index.html
- https://www.wired.com/story/drone-altitude-limits-explained/

