The first drone was flown in 1917, marking the beginning of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) in military applications. This pivotal moment set the stage for the evolution of drone technology, which has since transformed various fields such as defense, agriculture, and even commercial industries. In this article, we will explore the origins of drones, their evolution throughout history, and the profound impact they have had on numerous sectors over the years.
The Birth of Drones: Early Concepts

The concept of unmanned flight can be traced back to the 19th century, where early inventors began experimenting with aerial devices that could be operated without a pilot onboard. These efforts laid the groundwork for future innovations in aviation. One of the earliest examples is the “aerial torpedo,” a concept proposed in the late 1800s, although it never came to fruition.
The real breakthrough occurred during World War I with the development of the Kettering Bug. Designed by Charles Kettering, this early drone was essentially a flying bomb, intended for military use to strike enemy positions without putting pilots at risk. It was powered by a small engine and had a wingspan of over 13 feet. The Kettering Bug successfully flew in 1917, marking a significant milestone as one of the first true drones that could be remotely controlled and used for combat purposes.
World War I: Military Innovations
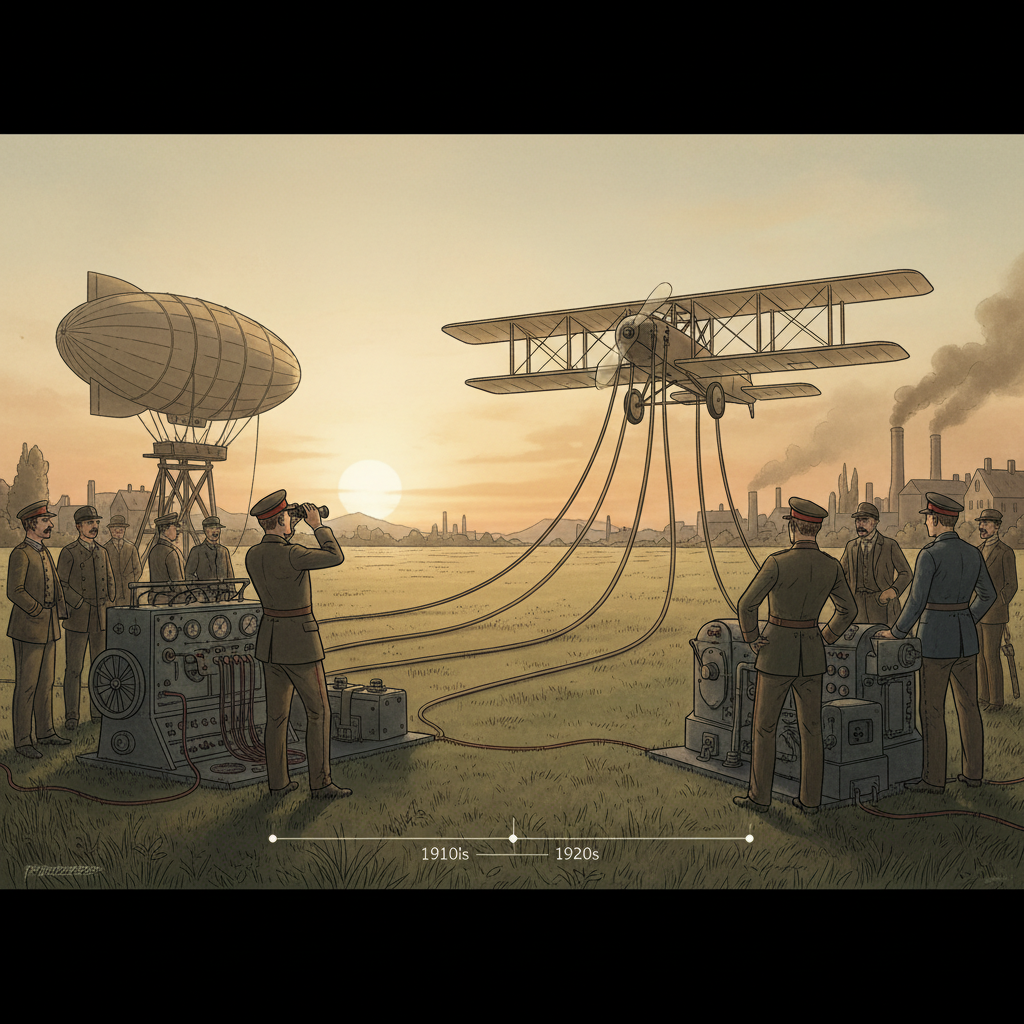
During World War I, the military recognized the potential of drones for reconnaissance and target practice. The initial focus was on developing UAVs that could provide vital intelligence without risking human lives. This led to the creation of several experimental drones, which were tested for their ability to gather information on enemy positions and movements.
The Kettering Bug was not the only innovation during this time. The development of radio-controlled aircraft began to emerge, with the military experimenting with various designs to enhance combat capabilities. Although these early drones were not widely deployed in combat, they laid the foundation for military strategies that would later fully embrace unmanned aerial technology.
The Interwar Years: Advancements and Challenges
The period between the two World Wars saw a slowdown in drone development, primarily due to technological limitations and a lack of military interest. The 1920s and 1930s were characterized by a focus on manned aircraft, as advances in aviation technology took precedence. Nevertheless, some experimental drones were tested, including the Radioplane OQ-1, which was a precursor to more advanced UAVs.
Despite the challenges, innovators continued to explore the potential of drones. The development of radio control technology advanced, paving the way for more sophisticated designs. However, the limited success of these prototypes meant that widespread use remained elusive, and military funding for drone projects dwindled during this time.
World War II: Expansion and Utilization
World War II marked a pivotal shift in the application of drones. The military began to utilize unmanned aircraft more extensively for training purposes and surveillance missions. Drones such as the Radioplane OQ-2, created by actor and inventor Howard Hughes, became the first mass-produced UAV in history. The OQ-2 was designed for target practice and training for anti-aircraft gunners, offering a safe and cost-effective way to simulate aerial combat scenarios.
As the war progressed, drones were employed for reconnaissance missions to gather intelligence on enemy forces, thus demonstrating their utility in warfare. Their ability to operate without risking human lives made them an attractive option for military strategists looking to gain an advantage on the battlefield. This period not only expanded the capabilities of drones but also reaffirmed their potential in military operations.
Post-War Developments: The Cold War Era
The Cold War era of the 1950s and 1960s saw significant advancements in drone technology, driven by the need for improved reconnaissance capabilities. The U.S. military began to invest heavily in UAV development, leading to the creation of advanced models such as the Lockheed D-21 and the Ryan Firebee. These drones were designed for high-altitude reconnaissance missions, capable of gathering critical intelligence over enemy territories.
As tensions between superpowers escalated, the strategic importance of drones became increasingly apparent. They were integral in monitoring missile sites and troop movements, providing essential information without the risk of human casualties. This period solidified the role of drones in military operations, setting the stage for more sophisticated UAV technologies in the following decades.
Modern Era: Drones in Civilian Life
Entering the 21st century, drones have transitioned from predominantly military applications to a wide range of civilian uses. The advent of commercially available drones has revolutionized industries, including photography, agriculture, and disaster response. For instance, drones are now widely used in agriculture for crop monitoring, allowing farmers to assess field conditions and optimize yields.
Moreover, they have emerged as valuable tools in disaster response scenarios, enabling rapid assessments of affected areas and supporting search-and-rescue operations. Drones have also found their way into the realm of entertainment and personal use, with hobbyists and professionals alike utilizing them for aerial photography and videography.
This shift has not only democratized drone technology but has also raised important discussions about regulation and safety, as the number of drones in civilian airspace continues to grow.
Future of Drones: Trends and Innovations
The future of drones is poised for continued growth and innovation, driven by emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), enhanced battery life, and improved sensors. AI integration is set to revolutionize how drones operate, enabling autonomous flight and advanced data analysis capabilities, which will enhance their utility in various applications.
Additionally, advancements in battery technology promise to extend flight times and increase payload capacities, making drones more versatile than ever. As these technologies develop, regulatory frameworks are evolving to address the challenges and opportunities posed by the growing use of drones in civilian airspace.
Policymakers are increasingly focused on establishing guidelines that ensure safety, privacy, and accountability in drone usage, balancing innovation with public concerns. As the drone industry expands, staying informed about these trends will be crucial for businesses and consumers alike.
In conclusion, the journey of drones from their first flight in 1917 to their current multifaceted applications reflects remarkable technological advancements. The evolution of drones showcases their transformative power across various fields, from military operations to civilian applications. Understanding this history not only sheds light on the capabilities of drones today but also helps us appreciate the potential they hold for the future. As drone technology continues to advance, it will undoubtedly play an increasingly pivotal role in shaping our world.
Frequently Asked Questions
When was the first drone flown and who invented it?
The first recorded instance of a drone being flown dates back to 1917 during World War I, when the U.S. military developed the “Kettering Bug,” a prototype unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV). This early drone was designed for use as a flying bomb, showcasing the initial military applications of drone technology. The Kettering Bug’s flight marked a significant moment in aviation history, paving the way for future developments in UAV technology.
What were the primary uses of early drones after their invention?
Early drones primarily served military purposes, mainly for reconnaissance and training. During World War II, drones were used as target practice for anti-aircraft gunners and as surveillance tools to gather intelligence on enemy movements. These initial applications laid the groundwork for the diverse uses of drones today, including commercial, recreational, and emergency services.
How have drone technologies evolved since the first flight?
Since the first flight of the Kettering Bug, drone technologies have evolved significantly, transitioning from basic, unmanned aircraft to sophisticated systems equipped with advanced sensors, GPS, and real-time data transmission. Modern drones are capable of performing a wide range of tasks, from aerial photography and agriculture monitoring to search and rescue missions. This evolution is driven by advancements in materials, miniaturization of components, and innovations in software.
Why is the history of drone development important to understand?
Understanding the history of drone development is crucial because it highlights the technological advancements and changing perceptions of UAVs over time. Knowledge of how drones originated and evolved helps contextualize their current applications, regulatory challenges, and social implications. Additionally, it sheds light on the ethical considerations and future potential of drone technology in various sectors, including logistics, healthcare, and environmental monitoring.
Which countries were the first to develop and use drones for military purposes?
The United States and the United Kingdom were among the first countries to develop and use drones for military purposes during World War I and World War II. The British developed the “Radioplane,” while the U.S. introduced the Kettering Bug. These early innovations in drone technology were pivotal in shaping military strategies and highlighting the potential of unmanned systems in warfare, influencing subsequent developments worldwide.
References
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Drone
- https://www.history.com/topics/inventions/drone
- https://www.bbc.com/future/article/20210517-the-history-of-drones
- https://www.nytimes.com/2021/07/27/technology/drones-history.html
- https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/technology/drones.html
- https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2020/aug/24/drones-history-uses
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352864821002618

